What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is a common type of skin cancer. It can develop anywhere on the body, although it most commonly appears on the face, the neck, and the back – the areas that are generally exposed to the sun the most. Like any other cancer, melanoma is an abnormal growth of cells that lack the mechanism for controlled growth. If detected early enough, the early-stage melanoma survival rate is around 99%.
Your skin may experience some changes due to old age, long-term exposure to the sun, or even exposure to some chemicals. Dr Mark Gittos FRACS(Plast) is a specialist Plastic Surgeon who works with clinics that can diagnose any changes on your skin, including melanoma. As a skin cancer expert, Dr Gittos can remove skin lesions with minimal scarring. He is internationally recognised in the UK and Europe as a leading specialist who has pioneered several surgical procedures used today. Dr Mark Gittos operates at clinics in Auckland (Herne Bay), Plymouth – Skin Centre Taranaki, Kensington Hospital Whangerei, and Tauranga clinic, where he performs skin cancer surgeries.
Risk Factors for Melanoma

There are several risk factors associated with Melanoma:
- lighter skin colour or fair complexion
- previous sunburns (especially heavy sunburns, such as after diving with no protective garments)
- moles
- a history of skin cancer in you or a family member
- exposure to certain chemicals (arsenic)
- radiation exposure
- excessive exposure to the sun, such as is found in agricultural workers, lifesavers or general people working outside, in direct sunlight
If you fall in any of these risk factor categories, you may want to check your skin every three months for any changes. Changes that you should look for include the appearance of new moles, changes in old moles, any localised pigmentation or changes in the skin texture. Not every change is melanoma, especially not a malignant melanoma, but the nature of the changes can only properly be addressed by a specialised plastic surgeon.
Identifying Skin Cancer
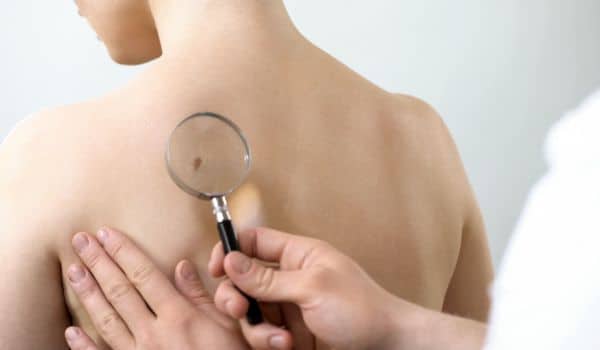
If you have noticed any changes in the colour, shape or pigmentation of your moles, you should consult a specialist to examine the changes. If you see any new localised pigmentation of the skin, strange swelling or changes which ooze, are itchy, sore or reddish in appearance, you should also consult a specialist. Your specialised plastic surgeon will be able to assess these changes and suggest proper treatment if needed. Dr Mark Gittos can perform the removal procedure of these changes and provide adequate aftercare advice for your highest comfort.
Different Kinds of Melanoma
There are several kinds of melanoma. You should understand that not every skin cancer is melanoma, as there are different types of cancers depending on the tissue they appear on. There are:
Melanomas represent a group of skin changes that can be life-threatening if not detected early enough and properly taken care of. They can be:
- Superficial Spreading Melanoma – this is a type that starts on the upper layers of the skin. It penetrates deeper only at later stages
- Nodular Melanoma – the first symptom is a nodule under the skin that is hard to touch. It grows quickly (the aggressive skin cancer melanoma)
- Lentigo Maligna Melanoma – common in the elderly with heavily sun-damaged skin
- Acral Lentiginous Melanoma – a rare form that appears on the palm and the soles. It can also be found under fingernails and toenails
- Amelanotic Melanoma – a type that is difficult to diagnose. This type of skin cancer cell produce little or no pigment
Dangers of Skin Cancer
Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer. If left untreated, it can spread to the surrounding tissues, which significantly complicates the procedure and reduces the chances of positive long-term outcomes of such practices. In some cases, once cancer has spread, it may be incurable. This is known as metastatic melanoma.
Skin cancers might be easily treated if they are detected early enough. The early-stage melanoma survival rate is around 99%, while in more advanced stages of cancer, it may even be incurable. In the USA alone, this type of cancer kills 9,300 people annually. Good skincare routine, continuous use of SPF with a sun protection factor of 30+ and above, and regular skin checks are the best measures that any adult should practice regularly. You may consult your GP or your specialised plastic surgeon for more information on proper skincare and schedule an appointment for a skin check.
Melanoma vs. Moles – What Is the Difference?
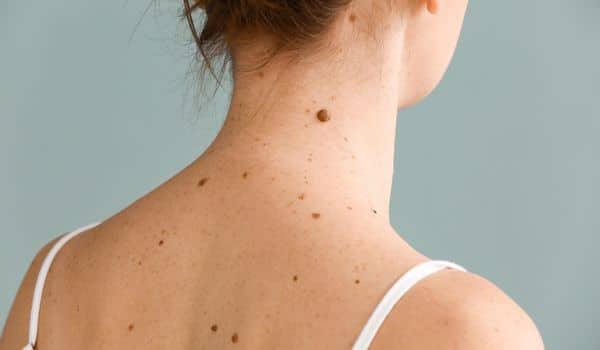
To easily distinguish between a melanoma and a mole, you should follow the ABCDE rule:
- A – Asymmetry. Most melanomas are asymmetrical. The two halves do not match, whichever way you may look
- B – Border. Borders of melanoma are not clear lines; they may look uneven, blurry or distorted
- C – Color. Moles are of one colour. Melanomas may display a colour variety across their surface, which can range anywhere between white, over red, to almost completely black
- D – Diameter / Darkness. Melanomas grow, so if you notice a growing mole, you should head to your doctor. Any change more than 6mm in diameter has to be checked by the doctor. Melanomas are usually darker than the surrounding tissue
- E – Evolving. Any change in shape, size or perceived depth can be an indicator of melanoma
Skin Cancer Removal Procedures
Melanoma treatment depends of various factors. Your experienced plastic surgeon, Dr Mark Gittos, will be able to properly assess your case and give advice on which approach may be the best in your case. The surgical procedures and non-surgical procedures that may be used during melanoma removal are:
- Surgical Excision – the specialised plastic surgeon will surgically remove the skin lesion. This is done under local anaesthesia or general anaesthesia if the lesion covers a large area of the skin
- Cryosurgery (freezing) – liquid nitrogen is applied to the lesion, killing off the cancer cells
- Mohs Surgery – thin layers of tumour and surrounding skin are removed. The procedure is repeated until healthy tissue is reached. This surgical procedure is most commonly used on the face
- Radiation Therapy – usually accompanies another procedure and is used to kill off any remaining cancer cells
- Chemotherapy – applied locally or generally, this therapy slows down the growth of skin cancer cells, giving your immune system more time to fight them off
- PTD (PhoToDynamic) Therapy – uses a combination of drugs and a laser to kill cancer cells
- Biological Therapy – drugs that stimulate your body’s immune system to attack cancer cells
Melanoma FAQs

What does a melanoma spot look like?
- A melanoma spot often has an irregular shape, darker in colour than the surrounding tissue and growing. It may appear in the place of a mole on your body, and in this case, it will usually look like a red ring around the mole in the initial stages of development.
How do you identify this type of cancer?
- Dr Mark Gittos, a specialised plastic surgeon, will be able to assess your changes and provide a professional diagnosis. Skin cancer identification means counting in several factors, such as the shape, size, colour, texture, skin complexity, lifestyle choices and habits, as well as your medical history and your family medical history.
How does Melanoma make you feel?
- This type of cancer may feel itchy and sore without any other symptoms in the early melanoma stage. In later stages, especially if you have a case of metastatic melanoma, the organs it has spread to may show signs of declining function, and you may feel tired.
Does this type of skin cancer show up in blood work?
- No, it does not show up in bloodwork. Your specialised plastic surgeon may order an LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) blood analysis if he suspects you may have a more advanced form of skin cancer.
Are skin cancers itchy?
- Yes, skin cancers can feel itchy. This is especially true for basal cell skin cancer, which may feel itchy and look similar to a healing wound. If you notice any such changes, consult Dr Gittos NZ, and schedule a check-up appointment.
Is this type of skin cancer flat or raised?
- Some melanomas are flat, and some are raised. Lentigo Maligna Melanomas first appear in upper skin layers and may develop as a flat change on the skin for a while. Melanomas that occur as the growth of cancer or precancer cells in moles will normally have a raised shape.
Is this type of skin cancer hard or soft?
- Melanomas are mostly hard to touch. The Nodular type will be hard to the touch and in the shape of a nodule under the skin.
Can a melanoma be white?
- Yes, amelanotic types are generally of lighter colours since they produce no pigment.
Is this type of skin cancer always black?
- No, it is not always black. Melanomas may range in colour from white, over purple, red, brown, to completely black. Some of them may even display a variety of colours.
Does it weaken your immune system?
- In general, it doesn’t weaken your immune system. In the case of late-stage melanoma, where metastasis is present, the overall deterioration of health may induce some changes to the way your immune system behaves.
Can it go away on its own?
- Yes, in some cases. Sometimes it can spontaneously regress without any treatment. This does not mean that you should wait to notice any changes on your skin: most of them do not spontaneously disappear.
What do early signs of this skin cancer look like?
- Early signs include changes in the skin, which are different in shape, size and colour. Additional symptoms which may appear include changes in the texture, itchiness, oozing from the change or even bleeding.
What are the five warning signs of malignant melanoma?
- Follow the ABCDE rule here: Asymmetry, Borders, Colour, Diameter, Evolving. – If any of these should be noticed, schedule an appointment with Dr Gittos.
How quickly can Melanoma appear?
- They can appear and spread very quickly. This skin cancer may become life-threatening in as little as six weeks as it spreads to the surrounding tissues.
What is early stage melanoma?
- Based on how much cancer has spread, it is divided into five categories, ranging from 0 to 4. 0 is the initial stage, where it is present only on a portion of the skin (usually a very small change). Stage 4 means that metastasis is present.
What is the most effective treatment for this type of skin cancer?
- Wide excision is the most effective treatment for melanoma. The specialised plastic surgeon will surgically remove the skin cancer and the surrounding skin during this procedure.
Does Stage 1 melanoma require chemo?
- Most probably not. Stage 1 melanoma mostly does not require additional treatments.
What does Stage 2 melanoma look like?
- Stage 2 melanoma is more than 1mm thick and may have spread to deeper skin layers. It has not spread to other parts of the body yet.
Can you have stage 4 melanoma and not know it?
- Yes. In some cases, even stage 4 melanoma may not give any symptoms. The change is detected through a scan.
How do you know what stage skin cancer you have?
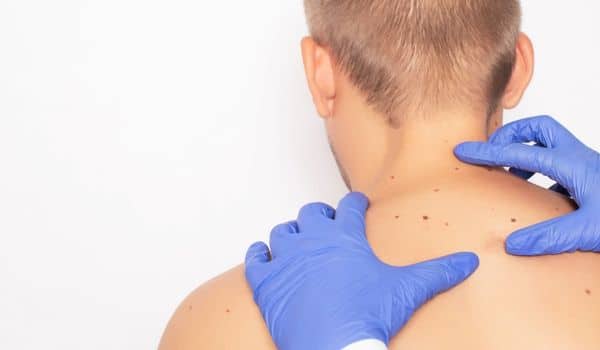
- After removal, your specialised plastic surgeon will examine the tissue removed. He may look at the thickness and other characteristics to determine the stage in the development of cancer. He may also order a full biopsy of the tissues.
Where does this type of cancer usually spread first?
- It may release some of its cells into the intercellular space. These cells are then carried by lymph to the nearest lymph node.
Can you tell if this type of skin cancer has spread?
- Yes and No. If it spreads only in the skin area, you may feel small nodules that increase in size and number over time. In some cases, the cancer cells may spread to deeper tissues where it can be difficult to tell they are there.
Can this type of skin cancer be cured?
- Yes, it can be cured. The 5-year survival rate in patients with early detection of changes is around 99%.
What should I eat if I have skin cancer?
- In general, keeping a healthy and well-balanced diet rich in fibres, antioxidants and zinc should be enough to keep your body healthy and happy. Your doctor may be able to give you some more advice on the exact peculiarities of your diet since some cases may require mild adjustments to suit better any medication you may be taking.
What can be mistaken for melanoma?
- Pyrogenic Granuloma, Dermatofibroma and Seborrheic Keratosis may be mistaken for melanoma.
What is the treatment for early stage skin cancer?
- Surgical excision is the best treatment for early stage melanoma. Various other procedures, such as cryotherapy, PTD therapy, and laser therapy, may be used in early-stage melanoma treatment.
Does vitamin D prevent skin cancer?
- High vitamin D concentrations have been proven to slow down the progress of melanoma and improve patients’ survival rates.
Further Reading about Skin Cancer
- Skin Cancer Removal Procedures
- Sun Protection Tips for Reducing Your Skin Cancer Risk
- Types of Skin Cancers and Their Causes
Medical References
- Skin Cancer / Melanoma Center: Signs, Treatments, Symptoms, Types, Causes, and Tests
- Mayo Clinic: Melanoma Pictures
- Video Melanoma Check
- Melanoma – Symptoms and causes
Next Steps
If you belong to any melanoma risk groups, you may want to schedule your first consultations with Dr Mark Gittos. You may schedule a full skin check, where any changes on your skin will be assessed and analysed to exclude the possibility of cancerous skin changes. If any such changes are noticed, Dr Gittos will schedule the procedure and inform you of any other steps that you should undertake to ensure a fast and safe recovery. Dr Mark Gittos operates in Plymouth – Skin Centre Taranaki, Kensington Hospital Whangerei, and Tauranga clinic. For more information on melanoma, see what Dr Mark Gittos NZ has to say about melanomas.
About Dr Mark Gittos FRACS (Plast) – New Zealand Plastic Surgeon
Practice locations in Herne Bay Auckland, Northland and Bay of Plenty – Kerikeri, Whangarei, New Plymouth & Tauranga
Dr Mark Gittos is a leading Specialist Plastic Surgeon and operates a practice in Herne Bay, Auckland and in the UK. The practice focuses on both surgical and non-surgical procedures, each designed to help restore, improve or change a physical characteristic or problem. The first step in every case is to talk through your personal requirements and explore all the options, before deciding on the most effective solution.
Dr Mark Gittos offers high quality, natural-looking cosmetic surgery results and is highly experienced in Breast, Body and Face Surgery having performed over 4000 Surgeries in the last 26 years. With worldwide expertise Dr Gittos is an expert in breast, face and body surgery for men & women.
Naturally, before any treatment is begun, we will explain clearly the advantages and risk factors; so that you have the information you need to make an informed decision that is best for you. Visit the practice to find out more.

NEXT STEPS
Please NOTE: Dr Gittos only performs surgery on non-smoker patients with a BMI less than 30. To check your BMI please visit the NZ Heart Foundation website. For help giving up smoking before surgery visit the Smoke Free website
Do your Research
- Read the Website and Blogs relevant to your procedure
- Browse our Frequently Asked Questions including how to choose a Surgeon for your procedure
- Download and read the FREE Guides to Surgery
What to Bring to your Plastic Surgeon Consultation
- Bring a friend or relative to help discuss the information and your choices
- Take lots of notes and read the documents provided thoroughly
- Dress in simple clothes as you may need to undress for examination
- Bring your medical referral and any relevant medical documents or test results
Book your Initial Surgery Consultation
- A Referral from your GP or specialist is helpful but NOT essential – you can have a consultation without a GP Referral
- Email us or Call on 09 529 5352 to arrange your surgeon consultation appointment.
- Book a consultation with Dr Gittos by paying the Consultation Fee – $350 incl GST
Traveling for Surgery? – Consider post-surgery luxury recovery in a Hotel with LuxeCare
Please contact us to arrange to book a consultation with our Specialist Plastic Surgeon or to speak with our Patient Care Advisor.
Send an enquiry form today or phone 09 529 5352 during Clinic Hours
